[Technical dry goods] The basic principle of the comparison series of LENS and SLM metal 3D printing technology and the comparison of molten pool shape
Laser additive manufacturing high-performance metal parts technology has the characteristics of complex molding structure, high molding precision and excellent molding performance. It is the most promising application technology for the one-time integral forming of complex precision metal parts or large-size main bearing metal components. One of them is not only a useful complement to traditional processing methods such as casting, forging, welding and machining, but also opens up a brand new metal part manufacturing model with important strategic research significance. At present, laser additive manufacturing high-performance metal parts technology mainly has two typical methods, one is based on laser powder deposition technology LENS (Laser Engineered Net Shaping), and the other is powder-based selection laser SLM (Selective Laser Melting).
Introduction to LENS principle
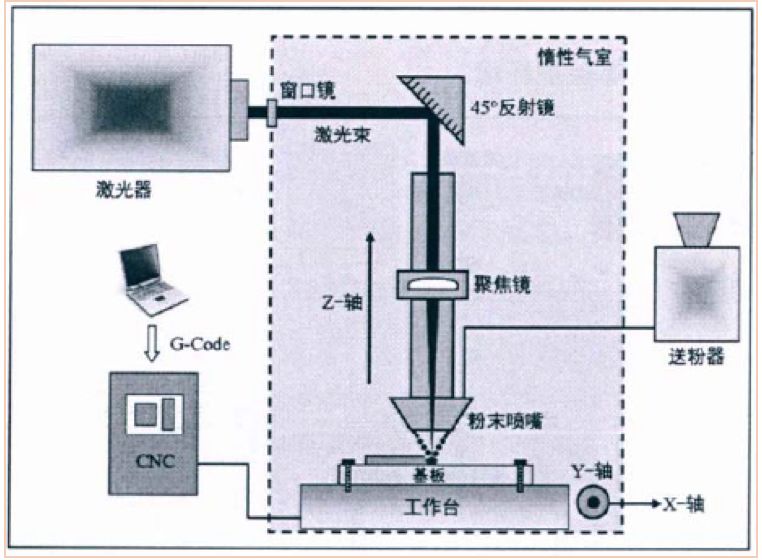
Firstly, the principle of the two technologies is briefly explained. The LENS focused laser beam is controlled and moved according to a preset path. At the same time of moving, the powder nozzle directly transports the metal powder to the melting of the laser spot on the solid substrate. The pool is solidified from point to line and from line to surface to complete the printing of a layer section. This layer is superimposed to create a near-net shape component entity.


Introduction to SLM principle
The forming principle of SLM technology, using a scraper to lay a layer of metal powder on the substrate, and then rapidly irradiating the powder according to a certain path under the control of the scanning galvanometer, causing it to melt and solidify to form a metallurgical cladding layer, and then The substrate is lowered to the same height as the thickness of the single layer deposition, and a layer of powder is subjected to laser scanning processing, and the process is repeated until the entire part is molded.


Due to the difference between the molding method and the process parameters, the above two technologies have great differences in the forming base of some materials such as the shape of the molten pool, the cooling rate, the solidification structure and the mechanical properties.
Molten pool morphology comparison
Under the different process conditions of LENS and SLM, the shape and size of the molten pool are completely different, and the heat conduction mode and heat effect are different, which ultimately affects the microstructure and properties of the alloy. The difference between the cooling rate of the micro-spot SLM and the large-spot LENS process pool The maximum can reach 4 orders of magnitude, the size of the cooling rate determines the size of the grain, although the average volume of the two process crystal lattice increases with the increase of energy input, but the size of the crystal column has a different trend with the cooling rate.
In the molding process of LENS, the size of the columnar crystal and the cooling rate satisfy a linear relationship, while the columnar crystal size in the SLM process has a cubic function relationship with the reciprocal of the square root of the cooling rate, which is inconsistent with the traditional theory, plus the single direction of the molten pool. The directionality and the like make the LENS process easier to form a coarse columnar crystal structure than the SLM process.
The minimum basic unit in the process of forming the molten pool, the stability of the molten pool is guaranteed to ensure the stability of the microstructure of the finished part and the final microstructure of the molded part. In the SLM forming process, the spot diameter is sub-millimeter and the thickness of the single layer is relatively thin. The volume of the molten pool is small, and the morphology of the molten pool, especially the depth of the molten pool, shows a "small hole effect."
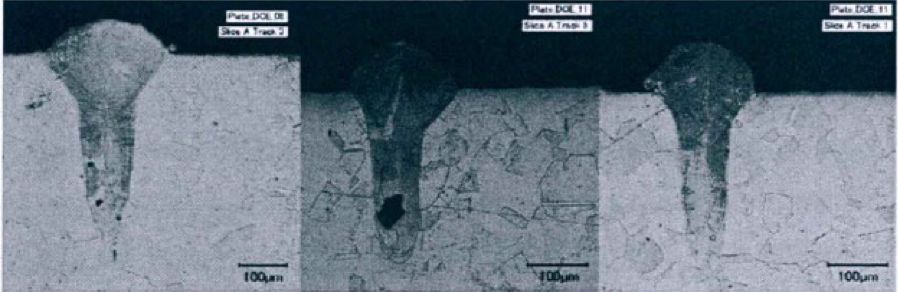
The large spot LENS process is generally formed with high power and large spot. Although the volume of the molten pool is increased, the depth of the molten pool is relatively small, and the penetration depth of the molten pool is relatively shallow, which is completely different from the SLM.

The following figure shows the longitudinal section of the molten pool under different processes.

Still not finished? Please listen to the next breakdown!
(three tribes MR.GAO edit finishing)
NINGBO ZHONGJIA ELECTRICAL APPLIANCE CO., LTD. , https://www.foodzhongjia.com