New pathway found in plants to regulate gibberellin synthesis
Motor protein (motor protein) is a type of protein that relies on cytoskeletal protein to convert chemical energy into mechanical energy, which is essential in the growth and division of animal and plant cells. But in addition to providing energy, it is not known whether these proteins have other physiological functions in animal and plant cells. The Research Institute of Plant Research and its collaborators discovered and confirmed that a kinesin-type motor protein has transcription factor activity, and its mutation leads to a decrease in gibberellin (GA) synthesis level, which hinders cell elongation.
The researchers found a mutant gdd1 in rice with significantly shorter seeds and organs. Physiological experiments showed that the mutant responded to gibberellin normally and exogenous application can restore its phenotype. Combined with genetic analysis, it proved that gdd1 For a new gibberellin synthesis defect mutation. The researchers isolated the GDD1 gene by map-based cloning, proving that the gene is located on chromosome 9 and encodes a kinesin-type motor protein BC12. Gene chip analysis showed that the transcription level of KO2, a key gene for gibberellin synthesis in the gdd1 mutant, was significantly down-regulated. Bioinformatics analysis, EMSA and ChIP proved that GDD1 can bind to the promoter of KO2 and has transcription factor activity. Therefore, the target gene of GDD1 is considered to be the key gene for gibberellin synthesis KO2. Further identification by capillary electrophoresis and mass spectrometry confirmed that the gibberellin synthesis in the mutant was reduced. This discovery reveals a new mode of gibberellin synthesis regulation and opens up a new avenue for the functional study of motor proteins in plant and animal cell growth and cell division. GDD1 gene has potential application prospects in molecular breeding.
Related research work was published in the international academic journal "The Plant Cell" on February 15 (thesis link: http: //). The research was supported by the Fund ’s Innovation Research Group Project and the National 863 Project.
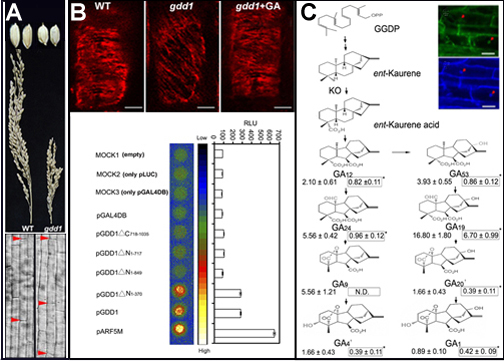
GDD1 mutations cause cell growth, KO2 gene expression, and gibberellin (GA) metabolism. A. Mutant seeds and ears and cell growth are blocked. B. GA restores the microtubule arrangement of mutants, and GDD1 has transcription activation activity. C. Localization of GDD1 and mutant GA metabolism.
Eva Bag,Eva Plastic Bag,Eva Mesh Beach Bag,Eva Zipper Packaging Bag
Dongguan Junkai Packaging Products Co., Ltd , https://www.diystoragecase.com